Indian government implements four Labour Codes
Move modernises labour regulations for future-ready workforce.
The Code on Wages, 2019; the Industrial Relations Code, 2020; the Code on Social Security, 2020; and the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020 are now effective in India.
According to India's Ministry of Labour & Employment, here's what the reforms mean for the country's workers and employers:
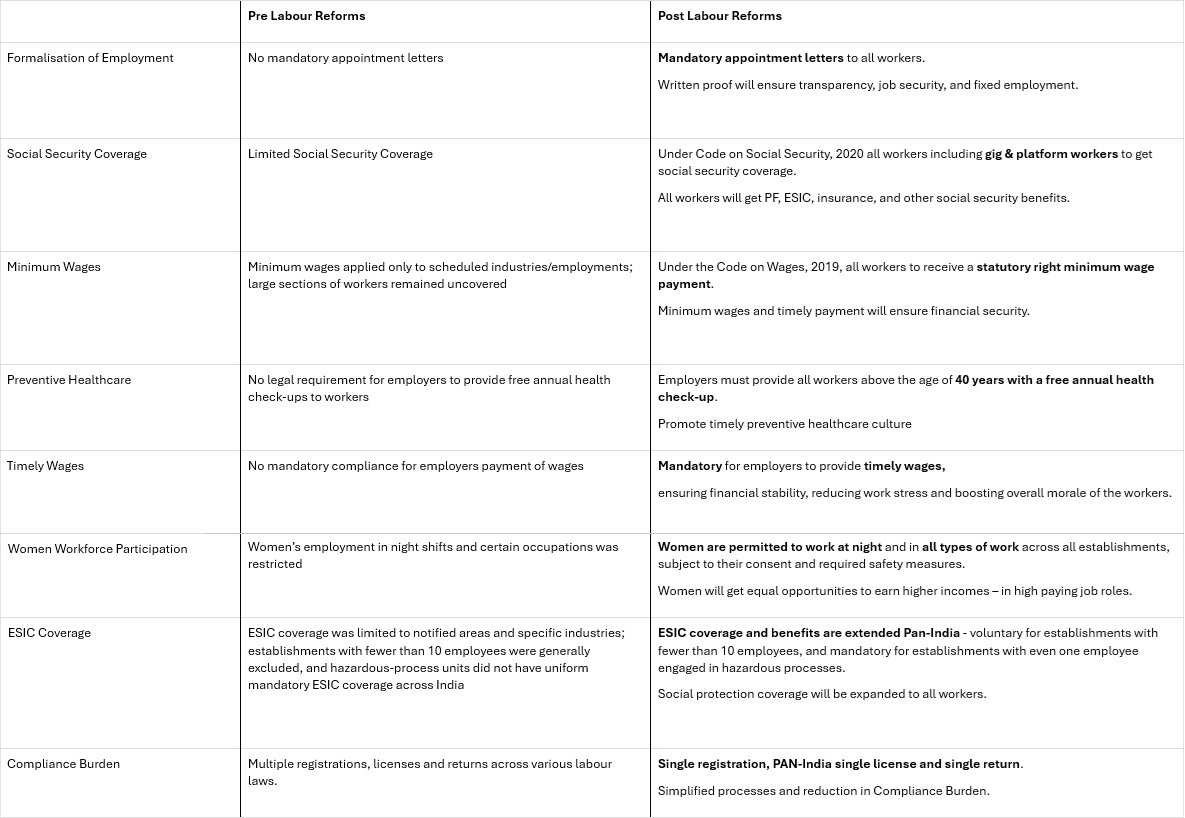
*click to enlarge
"By modernising labour regulations, enhancing workers' welfare, and aligning the labour ecosystem with the evolving world of work, this landmark move lays the foundation for a future-ready workforce and stronger, resilient industries driving labour reforms for Aatmanirbhar Bharat," the Ministry said.
Aatmanirbhar Bharat is the government's campaign aimed at making India self-reliant.
"Whilst most major economies have updated and consolidated their labour regulations in recent decades, India continued to operate under fragmented, complex, and in several parts outdated provisions spread across 29 Central labour laws," the Ministry noted.
"These restrictive frameworks struggled to keep pace with changing economic realities and evolving forms of employment, creating uncertainty and increasing compliance burden for both workers and industry.
"The implementation of the four Labour Codes addresses this long-pending need to move beyond colonial-era structures and align with modern global trends. Together, these Codes empower both workers and enterprises..."
Commenting on the development, professional services network KPMG called the implementation "a radical shift in the labour landscape" in India that seeks to create a more transparent and predictable environment.
KPMG stated: "Organisations may consider undertaking a comprehensive review of recent changes, implementing necessary policy-level adjustments, and proactively preparing for compliance obligations and operational realignments."